Virology: Introduction, Virus classification and Viral diseases
Introduction
- The branch of science that involves and deals with the study of viruses (submicroscopic, parasitic genetic material particles contained in a protein coat) and agents related to viruses, including their taxonomy, properties that produce diseases, and genetics are termed as virology.
- It is also considered a part of pathology and microbiology.
- Virology majorly focuses on different and various aspects of viruses like:
- Their structures.
- Evolution pattern.
- Classification under various categories.
- Its mode of action of entering host cells.
- Diseases caused by them.
- Isolation and characterization of viruses.
- Their numerous applications in therapy, research, and various industries.
Virus classification
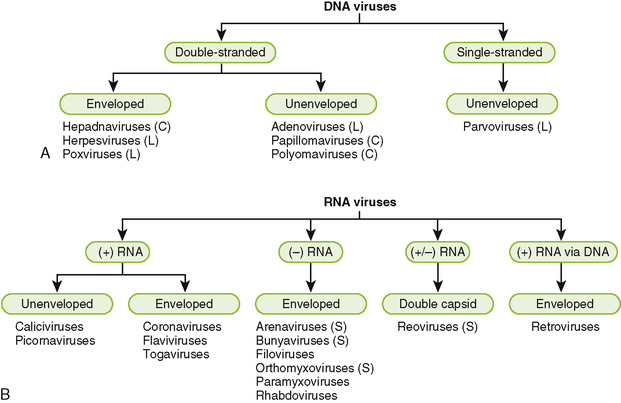
- The most useful and most frequently used system of classification identifies viruses by the type of nucleic acid they use as genetic material and the form of viral replication they use to coax host cells into creating more viruses:
- Viruses of DNA – divided into double-stranded DNA viruses and single-stranded DNA viruses.
- Viruses of RNA – divided into positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, negative-sense ssRNA viruses, and the much less common dsRNA viruses.
- Reverse transcribing viruses – Retroviruses, double-stranded DNA, and single-stranded RNA (all reverse transcribing)
- Subviral and infectious entities which are noticeably simpler and smaller than viruses are often studied by virologists:
- Viroid’s – These are RNA molecules that are circular and naked which are known for infecting plants.
- Satellites – These are nucleic acid molecules, with or without a capsid, which needed helper viruses to cause infections and to carry out reproduction.
- Prions – Infectious proteins particle, that can be found in pathological conditions).
Viruses usually come in small sizes (30nm – 450nm) which clearly indicates that they cannot be detected by light microscopes. Electron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, and NMR spectroscopy are widely used to investigate the structure and forms of viruses.
Viral diseases
- Viruses are widely present all over the earth and can be transmitted from one organism to another.
- They cause a series of significant infectious diseases, including:
- Common cold
- Influenza
- Rabies
- Measles
- Yellow fever
- Smallpox
- Dengue fever
- Diarrhea
- Hepatitis
- Polio
- AIDS
- Viruses act as a potential factor in Herpes Simplex, Alzheimer’s, which causes genital herpes and cold sores, is also under investigation.
- Viruses which responsible for the development of certain types of cancer, are known as oncoviruses.
- The best-studied example is the correlation between cervical cancer and human papillomavirus.
- The correlation of infection with hepatitis B and C viruses and cancer of the liver is another example.
- The degree to which diseases are caused by viruses is known as the virulence of the virus.
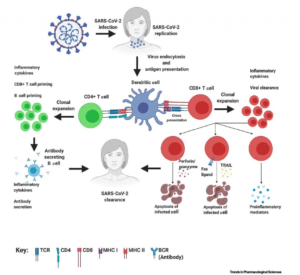
- Currently, the entire world is under the cusp of the COVID-19 coronavirus, which is also classified as a virus. It has symptoms similar to influenza, normal cough, and cold.
- Currently, the greatest researchers in the world are trying to come up with a vaccine for the cure of this viral disease, that caused a global pandemic.
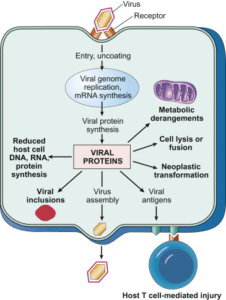
Host defenses against viruses:
Generally, humans use the following mechanisms to avoid infections:
- Natural Barriers: such as skin, mucous (coated on epithelium), bile, etc.
- Non-specific immune responses: Cytokines which include Interferons and natural killer cells(NKC) etc.
- Antigenic-specific immune responses: T cell, B cell, and antibody activities.

Reference and Sources
- https://www.answers.com/Q/What_is_a_very_small_plant_or_animal_which_causes_disease
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-microbiology/chapter/subviral-entities/
