Electrophoresis: Overview, Principles and Types
- Electrophoresis involves the migration of charged particle or molecules under the influence of an applied electric field.
- Various important biomolecules such as peptides, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acid and nucleotides has ionizable groups and they exist in solution as electrically charged particles either as cations or as anions at any given pH.
- These charged particles will move towards the cathode or to the anode end based on their net charge in a mixture under the influence of an applied electric field.
- The Rate of migration of charged particles depends upon following factors:
- The strength of electric field, shape and size.
- Relative hydrophobicity of the sample.
- Temperature and Ionic strength of the buffer.
- Molecular mass of the taken biomolecule.
- Net charge density of the bio molecule taken.
- Shape of the taken biomolecule.
Electrophoresis is basically of two types
- Free boundary or moving boundary electrophoresis.
- Zone electrophoresis.
Moving boundary electrophoresis
- It is a type of electrophoresis without supporting media, in a free solution.
- Tiselius developed this type of electrophoresis in 1937.
- For the separation of different charged molecules in a mixture, sample is placed in glass, which is connected to the electrodes. On applying electric potential across the tube, charged molecule migrates towards one or another electrode.
Zone electrophoresis
- It involves the separation of charged particles on inert matrix, or supporting or stabilizing media.
On the basis of supporting media, it is of following types
- Paper electrophoresis
- Cellulose acetate electrophoresis
- Capillary electrophoresis
- Gel electrophoresis.
The equipment used for the electrophoresis basically consists of two items:
An electrophoretic unit and a power pack.
Electrophoretic unit is of two types:
- Vertical electrophoretic unit
- Horizontal electrophoretic unit
Vertical electrophoretic unit
- It is also known as vertical slab gel units.
- It is available commercially and mostly used to separate proteins in acrylamide gels.
- In this, gel is formed between the two glass plates that are clamped together but uses plastic spacers to hold them apart.
- Dimensions of gel are typically: 8.5 cm wide X 5 cm high, Thickness = 0.51 mm.
Horizontal electrophoretic unit
- In this, a gel is cast on a plate, horizontally and submerged in a running buffer.
- This apparatus is mostly used to separate nucleic acid or proteins in agarose gel.
Paper electrophoresis
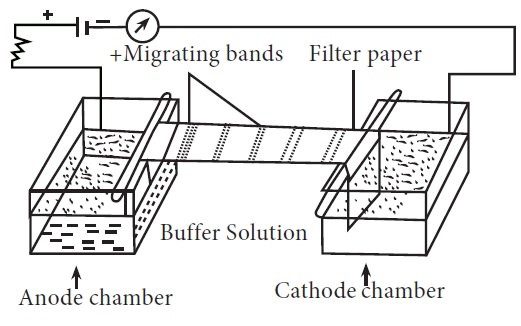
- Filter paper is very popular as a stabilizing media and most commonly used for the study of normal and normal plasma proteins.
- For electrophoresis Chromatography paper is most suitable and it needs no preparation other than to be cut to size.
- Apparatus: It consists basically of two items, a power pack and an electrophoretic cell.
- The power pack provides a stabilized direct current and has controls for both voltage and current output. Power packs, which have an output of 0-500 V and 0-150 rnA are available and can be programmed to give either constant voltage or current.
Cellulose acetate electrophoresis
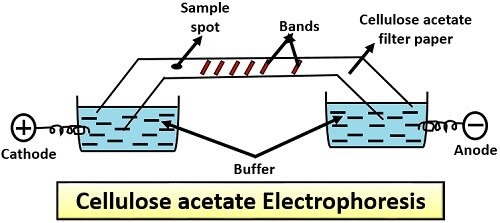
- Kohn in 1958 introduced, Cellulose acetate as a medium for electrophoresis.
- It was developed from bacteriological cellulose acetate membrane filters and is commercially available as high purity cellulose acetate strips, which are thin and have a uniform micropore structure.
- Cellulose acetate is especially used for clinical investigations such as separation of hemoglobin’s from blood, lipoproteins and glycoproteins.
- Buffers used in both the electrophoresis i.e., in paper and cellulose acetate electrophoresis are same
Capillary electrophoresis
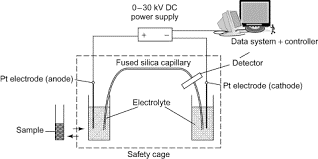
- It can be described as the new generation electrophoretic technique.
- Commercially available CE instruments consist of
- An electrolyte-filled capillary, which passes through the optical center of a detector
- A sample injector
- A high voltage power supply
- an auto-sampler. The entire instrument is computer controlled.
- This technique of electrophoresis has become very popular over the years because of the many advantages that it has over conventional electrophoresis techniques.
These advantages are listed below:
- Very high-level automation is possible.
- Fast analysis times.
- Detection of separated peaks is done online; thus, detection is a process that goes hand in hand with separation and not post-separation as is the case with conventional techniques.
- Heat generated inside the capillary is effectively dissipated through the walls of the capillary; therefore, high voltages can be applied.
- High voltages mean a rapid separation.
- This faster separation along with online detection makes this technique considerably faster as compared to the conventional techniques.
Gel electrophoresis
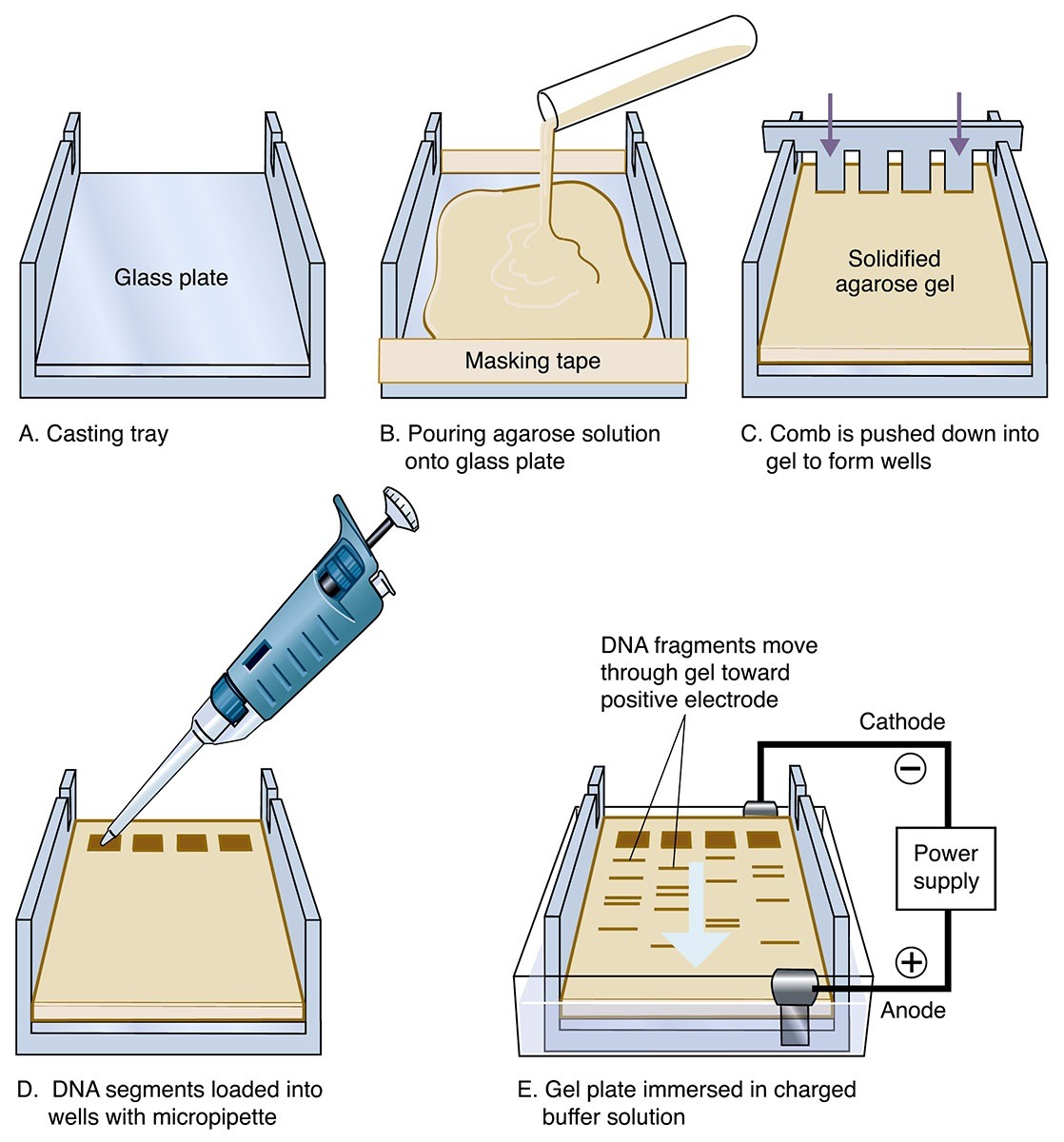
- It is simple, rapid and sensitive analytical technique for the separation of charged particle.
- The gels, however, are porous and the size of the pores relative to that of the molecule determines whether the molecule will enter the pore and be retarded or will bypass it. The separation thus not only depends on the charge on the molecule but also on its size.
- That resolution of a sample is sharper and better in a gel than in any other type of medium.
- Gel electrophoresis uses the gel as supporting media for separation of DNA, RNA and protein under the influence of electric charge.
Basically, gel electrophoresis apparatus is of two kinds:
- Vertical gel apparatus: It is commonly used for the separation of proteins in SDS-PAGE.
- Horizontal gel apparatus: It is used for immune electrophoresis, iso-electric focusing and electrophoresis of DNA and RNA in the agarose gel.
Type of gel electrophoresis:
- Agarose gel electrophoresis
- SDS-PAGE
- Pulse field gel electrophoresis (PFGE)
- 2D gel electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis
- The supporting media in this type of electrophoresis is agarose gel.
- It is routinely used for the electrophoresis of nucleic acid like DNA and RNA.
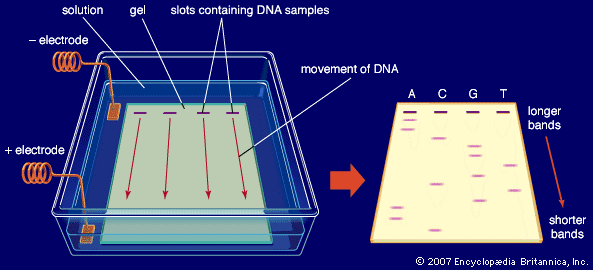
Principle
When potential difference is applied across the electrodes in a horizontal electrophoretic tank containing agarose gel and biomolecules (such as nucleic acid) is loaded, then molecules separated accordingly by their molecular size and move to their respective electrodes which is tracked with the help of dye.
Chemical component such as:
- Media: agarose gel
- Buffer: TAE/TBE (tris acetate EDTA/ Tris borate EDTA).
- Dye: EDTA
SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis
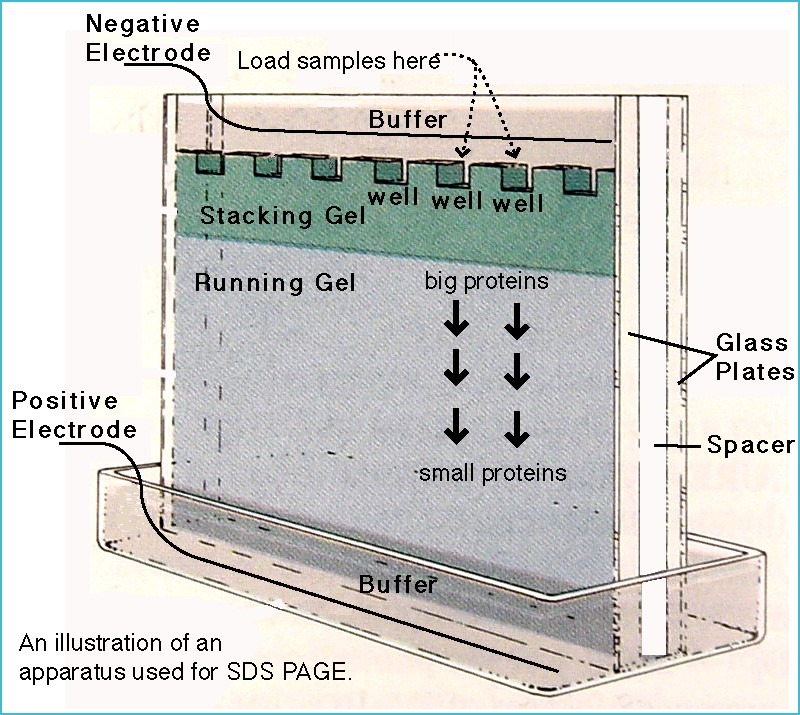
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is mainly used for the separation of proteins based on their mass.
- Principle: This technique uses anionic detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) which disassociates proteins into their individual polypeptide subunits and gives a uniform negative charge along each denatured polypeptide. When these denatured polypeptides are loaded at the cathode end of an electric field, then we get clear bands of proteins arranged in decreasing order of their molecular mass from the cathode to anode.
- To separate proteins it involves the use of vertical gel apparatus.
Chemical component
- Media: SDS-PAGE
- Buffer: lower reservoir: amine buffer with HCl (running gel), Upper reservoir: amine buffer with glycine (stack gel)
- Stains or dye: Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 (CBB) – anionic dye.
Pulse field gel electrophoresis
- It is using to separate large DNA molecule by applying gel matrix as electric field that periodically changes direction.
2D gel electrophoresis
- It is type of gel electrophoresis, which is generally using to analyze proteins.
Reference and Sources
- https://www.biotechnologynotes.com/electrophoresis/electrophoresis-meaning-definition-and-classification-withdiagram/293
- https://www.slideshare.net/AmruthaHari1/electrophoresispaper-electrophoresisgel-elctrophoresis-pagesds-andnonsds
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/electrophoresis-principle-affecting-factors-and-types/
- ttps://biocyclopedia.com/index/biotechnology_methods/electrophoresis/electrophoresis01.php
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/electrophoresis
- https://www.slideshare.net/DipeshTamrakar2/electrophoresis-79640318
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulsed-field_gel_electrophoresis
- http://lmxq.cper.revitradio.co/zone_electrophoresis_ppt.pdf

Useful. Thank u 😇