Introduction
- The cyanobacteria are the most important and most diverse group of photosynthetic bacteria.
- Cyanobacteria are Gram negative bacteria.
- They are obligate photolithoautotrophs and oxygenic photosynthetic.
- The only organism that can do nitrogen fixation and are able to perform oxygenic photosynthesis.
- Cyanobacteria also referred as blue green algae.
- Photosynthetic pigments present in cyanobacteria are chl a (in very few cases chl b and chl d), carotenoids and phycobilins (phycocyanin and phycoerythrin).
Occurrence
- Cyanobacteria are ubiquitous, and are often found in all types of environment-freshwater, salt marshes, hot springes, tree trunks, sea water, moist rock, frozen water, moist soil.
Morphology
- Cyanobacteria are varying greatly in shape and appearance.
- They range in diameter from 1 to 10 micrometres.
- Both unicellular and filamentous (termed trichomes), forms of cyanobacteria occur in nature.
- Filamentous form may be branched or unbranched.
- Trichomes is a row of bacterial cells that are in close contact with one another over a large area.
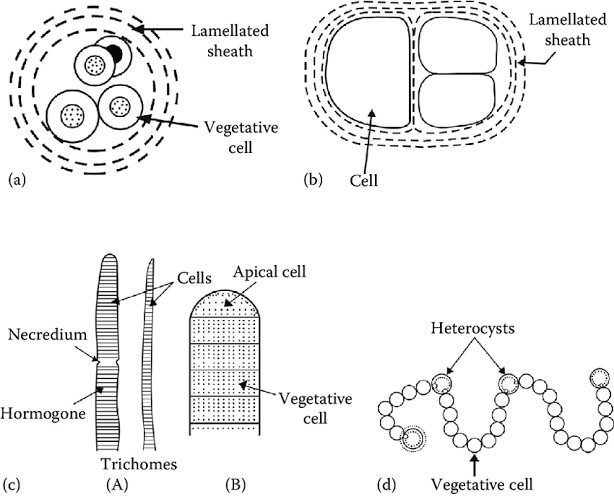
Single trichome filamentous may be of two types:
-
- Homocystous- Undifferentiated e.g. oscillatoria.
- Hetrocystous- Differentiated and having hetrocyst. E.g. Nostoc.
- Spirulina has a spirally coiled filament.
- Gliding movement is used by number of known cyanobacteria because flagella are absent.
Cell structure of cyanobacteria
- All cyanobacteria except Gleobacter violaceus, have an internal system of thylakoid membrane in which the light reaction of photosynthesis and respiration occur.
- Besides the thylakoid membrane the cyanobacteria cytosol contains components such as carboxysomes, glycogen granules, cyanophycin granules, lipid bodies, polyphosphate bodies.
- Cyanobacterial cells are more elaborate and larger than bacteria.

- It have typically prokaryotic cell structure naked DNA, 70s ribosome, one envelope organization with peptidoglycan.
- Membrane bound structure like endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, SAP vacuoles, plastids are absent in cyanobacteria.
- It’s cell wall is four layered with peptidoglycan is present in the second layer.
Reproduction
They employee’s variety of mechanism with respect to reproduction:
- Binary fission.
- Budding.
- Fragmentation.
- Multiple fission.
- Fragmentation of filamentous cyanobacteria form small, motile filaments called hormogonia.
- Some cyanobacterial species develop akinetes, specialised, thick- walled dormant resting cells that protect the organism in unfavourable conditions.
- They lack the enzyme alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, thus they do not have a fully functional citric acid cycle.
Heterocyst
- Many nitrogen fixing, filamentous cyanobacteria have specialised cells in which nitrogen fixation occurs known as heterocyst.
- It has enzyme nitrogenase.
- Heterocyst depends on adjacent vegetative cells for its nourishment.
- Photosystem II is absent.
- Thick walls present which is impermeable to oxygen but permeable to nitrogen.

Economic importance of cyanobacteria
- Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria are often used for reclaiming user soils. E.g. Nostoc, Anabena.
- Blue-green algae used as food for several aquatic animals.
- In Africa, spirulina is regularly collected for human consumption. Nostoc is similarly used in China as a food.
- From extract of, Lyngbia several antibiotic can be manufactured.
- Several species of cyanobacteria are used to prevent the growth of mosquitoes Larvae Nearby E.g. Anabena, Aulosira.
- Some produces some toxins which may be very harmful to most of the aquatic animals. The important toxins producing are: Microcytic aeruginosa, Anabena flosaquae.
Reference and Sources
- 1% – https://www.biologydiscussion.com/bacteria/cyanobacteria/cyanobacteria-classification-reproduction-and-parasexuality/54803
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11666410 _Proteins_ of_the_cyanobacterial_ photosystem_I
- 2% – https://www.biologydiscussion.com/bacteria/cyanobacteria/cyanobacteria-occurrence-morphology-and-cell-structure/52036


2 thoughts on “Cyanobacteria: occurrence, morphology, structure, reproduction”
HELLO..i need to learn about this bacteria
You can learn bhai