ELISA – Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
Introduction
- Immunoassays are bioanalytical methods, used to detect antigen-antibody specific reactions and provide qualitative /quantitative analysis in biological samples.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, commonly known as ELISA or EIA is a type of immunoassay and modified version of classic radioimmunoassay i.e., instead of radioisotopes, enzymes have been replaced (considered safe than RIA).
- For ELISA, a number of enzymes are used, which include alkaline phosphatase, horseradish peroxidase, and β- galactosidase.
- ELISA is commonly used in clinical diagnosis, food testing, drug discovery, and monitoring.
Principle
- ELISA is based on antigen-antibody reactions, it represents the chemical interaction of antigen and antibody produced by immune cells i.e., leukocytes
- ELISA allows selective quantitative/ qualitative analysis of antigens which also includes protein, peptides, hormones, nucleic acids, metabolites.
- To detect molecule, enzyme labelled antibody or antigen is used.
- Antigen is immobilised on a microtiter plate, made up of polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene and rigid polystyrene.
- The primary antibody reacts with immobilised antigen, later detected with enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody. The presence of antigen is determined by the development of colour by using chromogenic substrates (e.g., Alkaline phosphatase, produce p– nitrophenol (Yellow colour) when p– nitrophenol phosphate is hydrolysed by enzyme, detected at 405 nm).
- Chemiluminescent substrates and fluorogenic substrates can also be used for more sensitive detection.
- Enzyme- substrates reaction completes within 30- 40 mins, the reaction is stopped by using sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, etc.
- A microtiter plate reader is used to detect, coloured and fluorescent products.
Types of ELISA
Each type of ELISA can be used qualitatively to detect the presence of antibodies and antigens. Even, the unknown concentrations of samples can be determined, by using a standard curve with known concentrations of antibodies or antigens.
- Direct ELISA was first developed in 1971, it set the base style for other types of ELISA with modifications. In this technique, antibody or antigen was immobilised on a microtiter plate, enzyme-conjugated antibodies were allowed to react followed by colour development with appropriate substrates which was measured.
- These are common types of ELISA that are generally used:
- Indirect ELISA
- Sandwich ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
Indirect ELISA

- Sample containing primary antibody (Ab1) or serum is added to the microtiter well coated with antigen and allowed to react with attached antigen to the well. [Fig – A & B]
- Free Antibody (Ab1) is washed, bound antibody-antigen is detected by adding an enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody, which binds the primary antibody (Ab1). [Fig C]
- Free secondary antibody, is washed and the chromogenic substrate is added for an enzyme.
- A specialised spectrophotometric plate is used to measure the amount of the coloured products formed by reading absorbance.
Uses
- Indirect ELISA is suitable to detect the presence of serum antibodies (disease-associated antibodies), against endocrine diseases, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the causative agent of AIDS ( Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndromes).
- For HIV antigen detection, in the assay, core proteins and recombinant envelope of HIV are adsorbed as antigen immobilised to wells.
- For individuals affected with HIV, serum antibodies will produce for viral protein and react with its epitopes.
- These serum antibodies can be detected by Indirect ELISA within 6 weeks of infection.
Sandwich ELISA
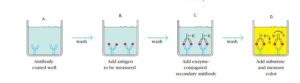
- Sandwich ELISA is used to detect or measure antigens.
- In this technique, primary antibody is immobilised on microtiter well plates [A] , when sample containing antigens is added , it reacts with immobilised antibody [B].
- After well is washed , enzyme conjugated secondary antibody specific for different epitopes is added , and permit to react with bound antigen. [C]
- After washing any free secondary antibody , substrate is added and coloured reaction product is measured.
Uses
- Used to detect macromolecules such as toxins or proteins.
- For instances, Ciguatoxins , causative toxins of ciguatera seafood poisoning , produced by marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus , can be detected by . monoclonal antiobodies in sandwich ELISA system.
- Marine biotoxins e.g., palytoxins can also be detected by sandwich ELISA.
Competitive ELISA

- The amount of antigen can be measured by competitive ELISA.
- In this technique, the primary antibody is first incubated in a solution containing the antigen. [A]
- Antigen-Antibody mixture is added to antigen immobilised to the microtiter well. [B]
- More antigens are present in the sample, less free antibodies will be present to bind to the antigen-coated well.
- The addition of enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody specific for isotype of the primary antibody used to determine the amount of primary antibody bound to the antigen-coated well, and coloured reaction products are measured. [C & D]
- In a competitive assay, absorbance is lower when the concentration of antigen in the original sample is higher.
Uses
- Both macromolecules and low molecular weight hapten can be detected by competitive ELISA.
Advantage of ELISA
- Simple Procedure
- High Specificity and sensitivity – Due to antibody-antigen reactivity
- High Efficiency- Complicated pre-treatment is not needed and simultaneously analysis can be performed.
- Considered safe and Eco- Friendly
- Cost-Effective Assays
Disadvantage of ELISA
- Antibody Preparations is an expensive and laborious process
- High possibilities of false-positive and negative.
- Antibody Instability
- Refrigerated transport and storage are required for antibodies.
References and Sources
- https://www.biologydiscussion.com/biochemistry/immunochemical-techniques/top-7-types-ofimmunochemical-techniques-used-in-biochemistry/12525
- https://www.learninsta.com/antigen-antibody-reactions/
- https://byjus.com/biology/elisa-technique/
Also Read:
- Agglutination reaction: Definition, Uses and Application
- Measurements of microbial growth
- Antibody or Immunoglobulin
- Immunoglobulin: Introduction, Structure and function
- Proteins: Definition, Roles, Functions and Structure
- Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
- DNA Replication in eukaryotes: Initiation, Elongation and Termination
- Vaccines: Definition, Types & Functions
- Milk: Composition, Processing, Pasteurization, Pathogens and Spoilage
- Enzymes: Introduction, Enzyme activity and work Mechanism
- Antigen-Antibody Reactions: Uses, Stages and Features
- Methods for Laboratory diagnosis of viral infections

I
It’s just so perfect I love it