Introduction
Antibodies, also called immunoglobulins (Ig), are glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes (plasma cells) in response to antigens. They play a central role in humoral immunity by recognizing and neutralizing pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
- Antibody antigen binding glycoprotein present on B-cell membrane and secreted by plasma cells.
- The term antibody was first used by the scientists Paul Ehrlich.
- Membrane on antibodies refers antigenic specificity on B-cells.
- Secreted antibodies circulated, where they act as enhancer for stimulation of humoral mediated response, to neutralize antigens from the system.
The main categories of antibody action include:
-
- Neutralization
- Agglutination
- Precipitation
- Complement activation
- All antibodies share structural features bind to antigen and participate in several functions.
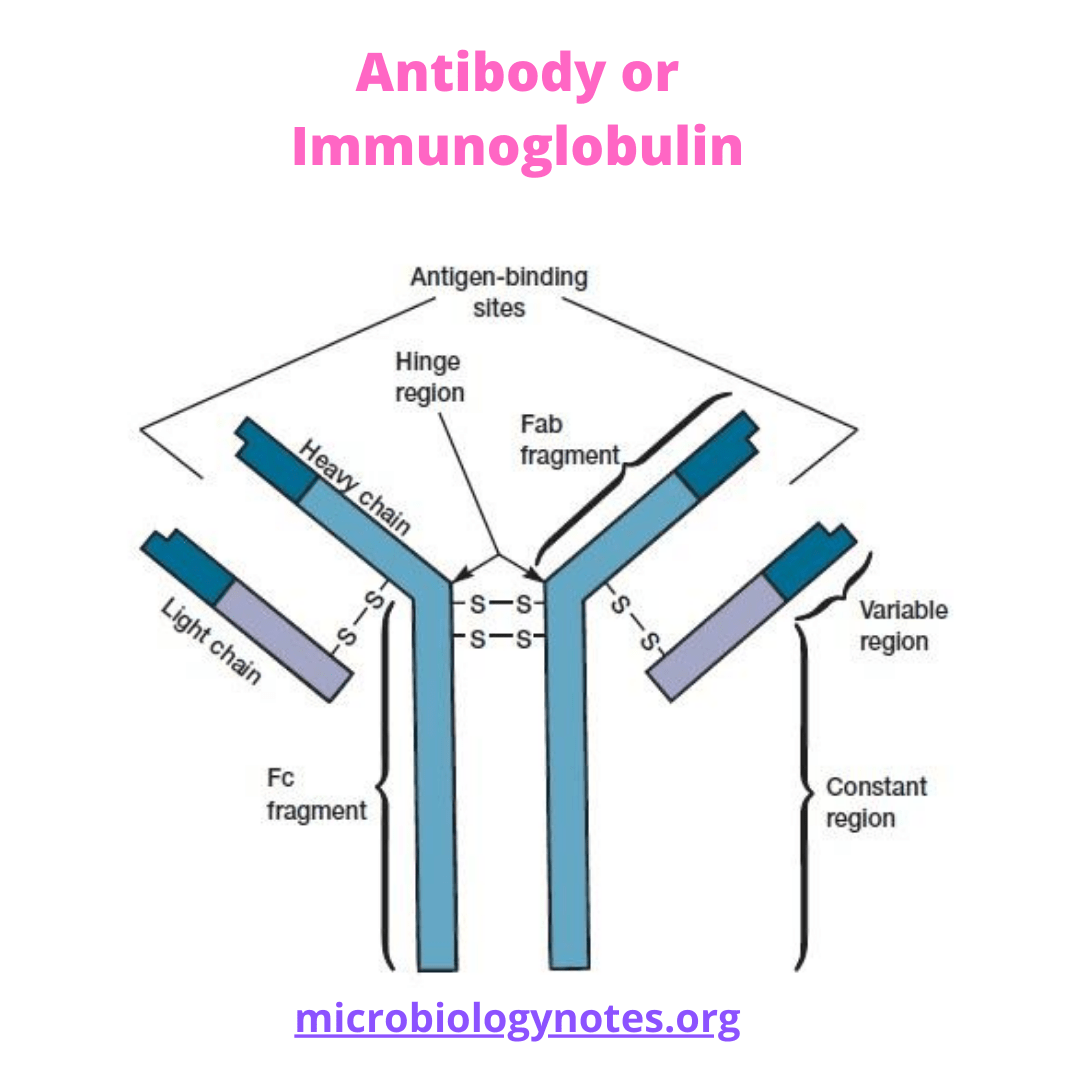
Structure of antibodies
- Antibody molecules have common structure of four polypeptide chains.i.e.2-light chains and 2 heavy chains respectively.
- Heavy chains consist of about 25000 molecular weight and light chain of 12000 molecular weight.

- Each Light chain is bound to heavy chain by non-covalent interaction.
- The light chain consists 220 amino acids while heavy chain consists of 440 amino acids.
- The Monomer has two kappa and two lambda
- Each antibody contains one or another type of light chains while consists of five types of heavy chains.
- Due to linkage of heavy chain and light chain antibody look like Y- shaped.
Types of antibodies
There are five classes of immunoglobulin molecules such as:
-
- IgG- Gamma
- IgA- Alpha
- IgE- Epsilon
- IgD- Delta
- IgM- Mu
- Heavy chains of antibodies had been named on Greek words each class of Ig plays important role in defense system.
IgG Antibodies
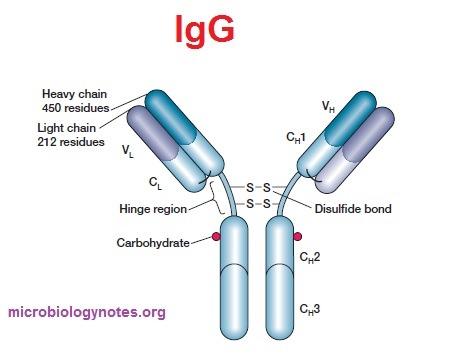
- 50 to 80% antibodies contribute in the form of IgG in our serum.
- The maternal molecules can pass through placenta and provide passive immunity to fetus.
- These can also pass the cell walls of blood vessel.
- They are Monomer and molecular weight about 1,50,000 KD.
- They are responsible for neutralizing microbes and their toxins.
- They also enhance effectiveness of phagocytic cells to engulf and ingest them.
IgM Antibodies

- They constitute about 5 to 10% in blood serum.
- It has pentamer structure.
- When expose to antigen, it is IgM that appears first.
- This specially cross linked particulate antigen and caused the aggregation due to numerous antigen binding site.
- Molecular weight about 900000 KD.
- It is very much effective as agglutination.
IgA Antibodies

- Concentration of IgA in human blood remains about 15%.
- It consists J- chain with dimer.
- Molecular weight is about 3,20,000 KD.
- It is present in blood serum and surface of lymphocytes.
- It checks the attachment of pathogens to mucosal surfaces and protect the infants from infections.
IgD Antibodies

- It accounts only 0.2% of serum.
- It is also Monomer and consist of 1,85,000 KD molecular weight.
- These are present on the upper surface of T- cells and it cannot pass across placenta.
- They assist initiation of immune responses and their population remains very high on the surface of the B – cells.
IgE Antibodies

- The concentration of IgE is 0.02% of the total antibodies.
- They are larger than IgG.
- It responses quickly to the receptor of the mast cells and basophils.
- Mast cell and basophils are spread cells that take part in allergic reaction.
- Molecular weight is about 2 lakh KD.
- They raise in infections and responsible for allergic symptoms.
Reference and Sources
- 2% – https://www.scribd.com/presentation/364594715/Immuno-Log-i
- 1% – https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/antibody-structure-classes-functions/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/286582202/mbc-chapter-17-adaptive-immunity-specific-defenses-of-the-host-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://silo.pub/essential-immunology-for-surgeons.html
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/21778281/microbiology-exam-4-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://www.klimud.org/public/atlas/idrar/web/www.irvingcrowley.com/cls/glossary_all.html
- 1% – https://www.rbldiagnostics.com/testmenu/

