Fungal Diseases
Content
- Introduction
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Dermatomycosis
Introduction
- Fungi are spore-bearing
- Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular.
- Mycology is a term used for the study of fungi and associated diseases.
Fungal diseases are of two types:
-
- Mycosis
- Food
Human infections are categorized into two types:
-
- Superficial infection
- Systemic infection
- Superficial infection include fungal growth from skin, nails and hairs.
- Various type of ringworm and several other fungal infections are seen on the body.
- Superficial mycosis are generally saprophytes and having capacity to digest keratin protein.
- Systemic mycosis is caused fungi which causes serious infection from general symptoms to fatal diseases.
Superficial infection is of two types:
-
- Surface infection
- Cutaneous infection
Some of the important fungal diseases are:
-
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Dermatomycosis
Aspergillosis
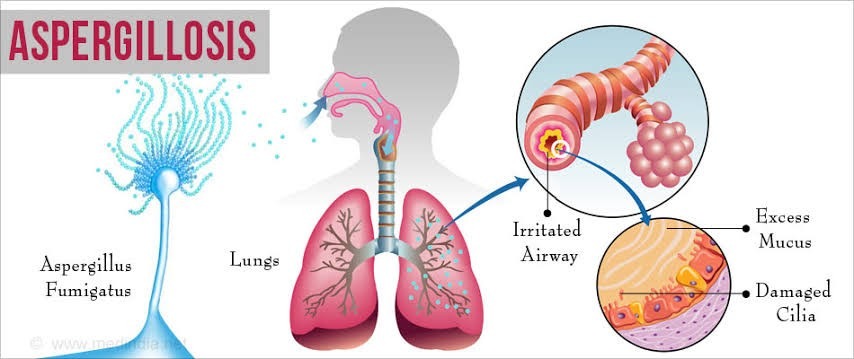
- Aspergillosis word given to large group of diseases caused by fungus infection from species Aspergillus.
- Aspergillosis is a disease occurs in humans, birds and other animals.
- The most important pathogens that are responsible for this disease are: Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus.
- It is chronic or acute forms.
Symptoms
- Coughing of blood
- Chest pain
- Infection in lungs causes cough, fever and chest pain.
- Kidney failure and liver failure.
Diagnosis
- On chest X-ray and CT, pulmonary Aspergillosis classically manifest as a hallow sign and later, as air crescent sign.
- On microscopy, aspergillus sp. are reliably exhibit by silver stains e.g. Gridley stain or Gomori methenamine silver, gives fungal walls grey black colour.
Treatment
- For aggressive invasive Aspergillosis include: Voriconazol, liposomal amphotericin B combination with surgical debridement.
- Iitraconazole
- Fluconazole
Epidemiology
- Aspergillosis is thought to affect more than 14 million people worldwide.
Candidiasis

- This fungal infection is caused by yeast belonging to genus Candida.
- There are about twenty Species of candida which can causes infection in human. the most common is Candida albicans.
- It normally lives on skin and mucous membrane without causing any infection. However, overgrowth of the strain causes infection as mouth or throat and systemic life-threatening diseases.
Symptoms
- Candida infection of mouth and throat can be seen as white patches/plaques.
- On the mucosal membrane including-redness, swallow and wound near the mouth.
Diagnosis and test
- The fungal strain is scrapped from the body and seen under microscope for confirmation of the pathogen to initiate the treatment.
- Generally, they are cultured on PDA and enriched media for confirmation of foreign agent or pathogen.
Treatment
Treated with antifungal medications
-
- Clotrimazole
- Nystatin
- Amphotericin B
- Caspofungin
Epidemiology
- Oral candidiasis is the very much common oral infection that occurs in humans.
- About 20% of those receive chemotherapy for cancer and 20% of with AIDS.
Dermatomycosis
- It is caused by various group of filamentous fungi affecting superficial skin, hair and nails.
- They are sometimes called skin lesion.
- They are generally including three strains.
- Trichodermaphyton
- Microsporum
- Epidermophyton
Reference and Sources
- 1% – https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fungus
- 1% – https://www.infectiousdiseaseadvisor.com/home/decision-support-in-medicine/infectio
us-diseases/superficial-mycoses-dermatophytosis/ - 1% – https://www.intechopen.com/books/immunodeficiency/fungal-infections-in-immunosuppressed-patients
- 1% – https://wikimili.com/en/Aspergillosis
- 1% – https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/candidiasis/index.html
- 1% – https://healthjade.net/what-is-candida/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/305509099/dermatophytes-cls-review-mycology-medical-laboratory-science-review-mycology-microbiology-fungi-mycology-assignments-flash-cards/
Also Read:
- Fungal Diseases of Hair, Skin, and Nails
- Introduction of Plant-Microbe Association and the Mycorrhizae
- Microbiology Disciplines: Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Archaea and Protists
- Histoplasmosis: Symptoms, Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention
- Second Golden Age of Microbiology
