Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Introduction
- In 1674 the classification of microbes was started with the invention of light microscope.
- Today it is a discipline which is based on the increasingly complex criteria.
- The first phylogenetic trees of life was constructed on the concept of just two kingdom’s: Plantae and Animalia.
- A German naturalist Ernest Haeckel in 1844 proposed that the bacteria, algae, Fungi and protozoa that lacks the tissue differentiation and be separated in a third kingdom protista and removed from the plant and animal kingdom’s.
- Prokaryotic cells are very simple, small in sizes however eukaryotic cells are very complicated, little larger structure and are present in trillions which might be single celled or multicellular.
This resulted within the division of those organisms into two groups:
- Prokaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic: pro- “old” and karyon- “nucleus”.
- This type of cells does not have nucleus.
- Most primitive type of cells.
- There are important to mankind in many aspects like they are utilized in fermentation research works, etc.
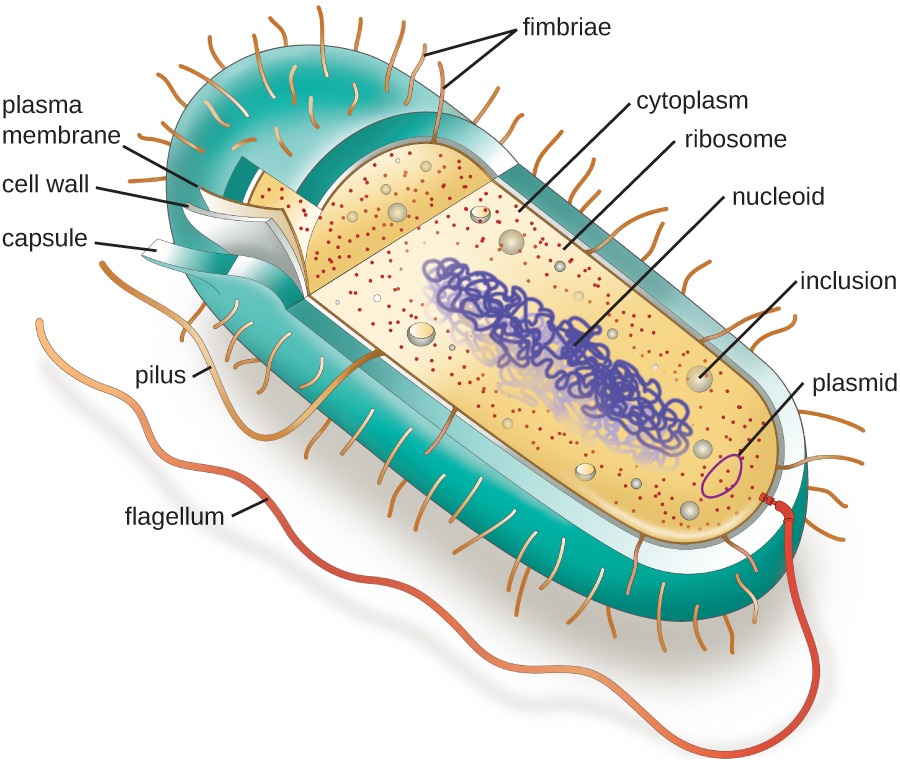
Generalised structure of prokaryotic cell consists of the following:
- Glycocalyx
- Nucleoid
- Cell wall
- Pilus
- Mesosome
- Flagellum
- Fimbrie
- Granules
- Ribosomes
- Cell membrane
- Endospores
Eukaryotic cell
- Eukaryotic: Eu- New, karyon- Nucleus.
- It is a type of cell which have a defined nucleus.
- It is advanced type of cells evolved from prokaryotic cell.

The general structure of eukaryotic cells is:
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Golgi apparatus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Appendages
- Surface structure
- Cell wall
- Cytoplasmic membrane
- Ribosome
- Cytoskeleton
| Features | Prokaryotic cells | Eukaryotic cells |
| Example | Bacteria | Algae, fungi, protozoa, plants and animals |
| Size range | 1-2 by 1-4 micrometers or less | More than 5 micrometers in width or diameter |
| Nature of cell | Unicellular | Multicellular |
| Genetic system location | Nucleoid, Chromatin body , or nuclear material | Nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast |
| Nucleus (structure) | Not bounded by nuclear membrane | Membrane bound |
| Nucleolus | Absent | Present |
| Histone Protein | Absent | Present |
| Sexual reproduction | Zygote nature is merozygotic (partial diploid) | Zygote is diploid |
| Cell division | Binary fission | Mitosis |
| Cytoplasmic streaming | Absent | Present |
| Pinocytosis | Absent | Present |
| Gas vacuoles | Can be present | Absent |
| Mesosome | Present | Absent |
| Ribosome | 70s , distributed in the cytoplasm | 80s, in endoplasmic; 70s, in mitochondria and Chloroplast |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplast | Absent | May be present |
| Golgi structure | Absent | Present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Membrane – bound (True vacuoles) | Absent | Present |
| Cytoplasmic membrane | Sterols is absent: carry out respiratory and photosynthesis | Sterols present: do not carry out respiration and photosynthesis. |
| Cell wall | Present, usually made up of Peptidoglycan (Murein or mucopeptide) | Only in plant cells and fungi. |
| Locomotor organelles | Simple fibril | Multi fibrilled with “9+2” microtubules |
| Pseudopodia | Absent | Present in some |
| DNA base ratios as moles% of guanine + cytosin (G+C)% | 28-73 | About 40 |
| Shape of DNA | Circular | Linear |
| Transcription and translation | Occurs together | Transcription in nucleus & Translation in cytoplasm |
Reference and Sources
- 1% – https://textarchive.ru/c-1198745-pall.html
- 1% – https://coolgyan.org/biology/prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells/index.htm
- 1% – https://bio.libretexts.org/Courses/Manchester_Community_College_(MCC)/The_Introduct
ion_to_Microbiology_(Cases)/05%3A_The_Eukaryotes_of_Microbiology/5.01%3A_Unique
_Characteristics_of_Eukaryotic_Cells - 2% – https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Prakash_Bisen/publication/263806602_Handbook_
of_Microbiology/links/559532f408ae5d8f392faf64?origin=publication_list - 1% – https://microbiologynotes.com/differences-between-prokaryotic-and-eukaryotic-cells/
- 1% – https://microbeonline.com/differences-prokaryotic-eucaryotic-cells/
Also Read:
- The Genetic Code
- DNA Replication in eukaryotes: Initiation, Elongation and Termination
- DNA replication in prokaryotes
- The Nucleus-Detailed Structure and Functions
- Bacteria: Shape, Size, Structure and other Membrane
- Membrane Structure, Its Related Proteins and Hydropathy Plot
