Introduction
- Riboflavin, also known as Vitamin B2 is a vitamin which is commonly found in food and used as dietary supplements.

- Vitamin B12 is that the Constituents of Flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and Flavin adenine dinucleotide(FAD).
- When phosphate is added in the Riboflavin FMN is synthesized.
- Transfer of an AMP moiety from ATP to FMN results in the formation of FAD.
- Food sources of riboflavin includes, eggs, green vegetables, milk and other dairy products.
- It is a that type of vitamin which is essential for the growth and reproduction of both humans and animals.
- It often employed as feed additive for the nutrition of various domestic animals.
MICROORGANISMS
- Various microorganisms can be employed for the fermentation production of riboflavin.
- It is a byproduct of the acetone butanol fermentation as carried out by microorganisms such as Clostridium butylicum, C. acetobutylicum.
- It is produced commercially by direct fermentation utilizing the ascomycetes Eremothecium ashbyii and Ashbya gossypii.
- Various candida species such as Candida flareri, Candida guilliermondia.
FERMENTATION
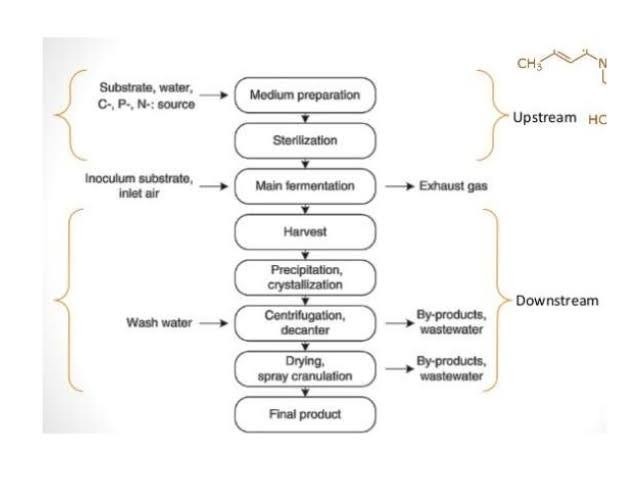
- Fermentation of the ascomycetes riboflavin utilizes media which contains a semi purified sugar like glucose, plus crude organic nutrients.
- Glucose could be totally replaced by a lipid such as corn oil, or a low level of corn oil and may be added to the glucose which may stimulates the yields of riboflavin.
- PH is adjusted 6 to 7.
- Ashbya gossypii fermentation is conducted at a temperature of 26 to 27˚C for 4 to 5 days.
- It is submerged and, fermentation is aerated but aeration should be avoided because excess air inhibits the production of mycelia and also reduces the yields of riboflavin.
HARVEST
- At harvest, the culture is evaporated and dried to serve as feed supplement.
- Those riboflavin fermentation utilizing species of candida are extremely sensitive to the presence of traces of iron and as a result iron or steel equipment cannot be used.
- Allowed the advancement by Kapralek (1962) and Starka (1957) for at least partial explanation. These workers demonstrated that the fermentation progresses through three phases.
- In the first phase, rapid growth with little production, glucose rapidly utilized and oxidized, pH Decreases because of pyruvic acid.
- In the second phase, sporulation occurs and pyruvate decrease’s in concentration, ammonia accumulate, rapid synthesis of cell bound riboflavin, occurring as FAD & FMN.
- In the last phase, autolysis occurs releasing free riboflavin into medium as well as riboflavin in the nucleotide form.
USES
- VitaminB12 is needed for growth and overall development and maintain good health.
- It helps to improve cardiovascular health.
- Riboflavin is vitamin which is required by the body for cellular respiration.
- Taking high doses of riboflavin reduce the number of migranic headache.
- This Supports eye health by maintaining healthy glutathione levels.
- It is also utilized for the development and function of skin.
Reference and Sources
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_B2
- 2% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238278249_Riboflavinaufnahme_und_-speiche
rung_durch_Zellen_der_flavinogenen_Hefe_Pichia_Candida_guilliermondii - 1% – https://optihance.com/product/optihance-nootropic1-neuro-brain-enhancer/
- 3% – https://spotlightonbusinessmagazine.com/%ef%bb%bfholistic-health-nutrients-a-to-z-vitamin b2-riboflavin/


1 thought on “Riboflavin: Fermentation, Harvesting and Uses”
Mispronounced as b12 actually it is b2