Aim
- To study and differentiate bacterial species from other negative cells using endospore staining technique.
- To observe capsule staining of capsulated bacteria by Maneval’s method.
Theory
- Bacterial endospore are metabolically inactive and highly resistant structures that are produced by some bacteria to defend the unfavorable condition.
- The bacteria have the ability to remain in the suspended state till the conditions are favorable enough to germinate and return to their vegetative state.
- During unfavorable condition, endospores can form within different areas of vegetative cell. The regions of endospore are central, terminal, sub-terminal and the shape may differ from elliptical to spherical.
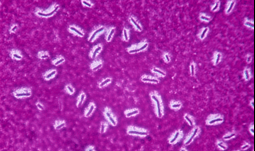
- The Schaeffer- Fulton stain is the most common endospore staining technique, which differentiates vegetative cell and the endospore.
- We will use malachite green, a primary water-soluble stain which is forced into the spore. To counterstain those cells which have been decolorized, a secondary stain safranin is applied.
- Therefore, at the end of staining, endospores will appears dark green, whereas, vegetative cells will appears pink.
Capsule staining
- It is a method in which acidic and basic dyes are used for staining the background and bacterial cells respectively so that the capsule can be visualized easily.
- Capsule is usually synthesized in the cytoplasm and secreted outside of the cell to surround the bacterium.
- Capsules are usually made of polysaccharides but some capsules are made of polypeptides too.
- The main principal of Maneval’s method is to stain the background using acidic solutions (congo red stain) and stain the bacterial cell using Maneval stain.
- Acid fushin being the main component of Maneval’s stain penetrates the exopolysaccharide layer with the help of phenol component.
Requirements
For Endospore staining
- Safranin
- Malachite green
- Bacterial suspension
- Distilled water
- Slides and blotting paper
- Inoculating loop
- Burner
- Microscope
For Capsule staining
- Congo red stain
- Maneval stain
- Bacterial suspension
- Distilled water
- Slides and blotting paper
- Inoculating loop
- Burner
- Microscope
Procedure
Endospore staining
- Take a clean, grease free slide.
- Air dry this particular smear and then heat fix it.
- Place the slide over steam bath and put a strip of blotting paper over the smear and stain it with malachite green stain for 3 minutes while this is in steam bath.
- Wash the slide and air dry.
- After air drying, add drops of safranin and let it stain for 5 minutes.
- Wash the excess stain and again let it air dry.
- Observe the slide under 100X objective lens after adding a drop of immersion oil.


Capsule staining
- Take a clean, grease free slide.
- Add a few drops of Congo red stain on its terminal and add few drops of bacterial suspension using micropipette.
- Spread the smear evenly throughout the slide at an angle of 45 degrees and let it air dry.
- Flood the slide using Maneval’s stain and let it rest for 5-6 minutes.
- Drain the excess stain and dry the stain gently suing blotting paper air dry it.
- After adding a drop of immersion oil, Observe the slide under 100X objective lens.

Reference and sources
- Https://id.scribd.com/doc/126340469/Microbiology-Lab-Manual-2
- Https://biologyreader.com/capsule-staining.html
- Https://microbiologyinfo.com/endospore-staining-principle-reagents-procedure-and-result/
- Https://www.scienceprofonline.org/vmc/vmc-lab-new-13/lab-3-differential-stains-specializedmedia/Differential-Stain-Microbiology-Lab-3-INSTRUCTIONS.pdf
- Https://askinglot.com/why-is-capsule-staining-called-negative-staining-method

